
ABS and HDPE are both common plastic materials, but they differ significantly in performance and applications. ABS is known for its high strength and impact resistance and is often used to manufacture electronic product housings and automotive components. HDPE, on the other hand, stands out for its excellent chemical resistance and moisture resistance and is widely used in pipes and packaging.
Although ABS and HDPE are both versatile plastics, they each have their strengths and weaknesses in practical applications. ABS is suitable for scenarios requiring high strength and durability, while HDPE is better suited for environments with high requirements for chemical resistance and moisture resistance. Next, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of these two materials in specific applications to give you a clearer understanding of their differences.
What are the differences in composition and structure between ABS and HDPE?
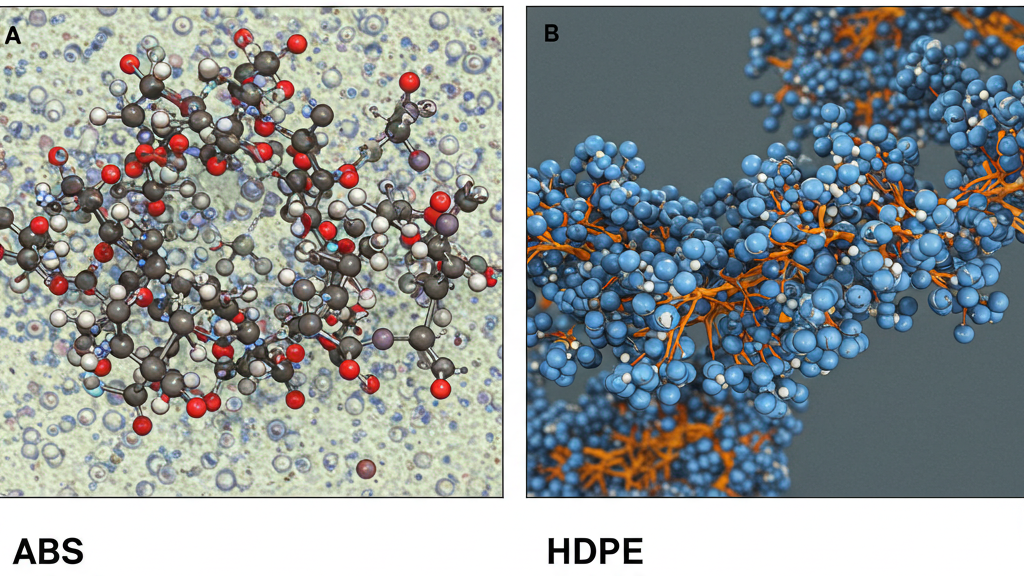
Although ABS and HDPE are both plastics, the differences in their chemical composition and molecular structure result in their vastly different physical properties. A deeper understanding of these differences will help us better understand the characteristics and applications of these two materials.
- Compositional Differences: ABS is a copolymer of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, making its composition complex. HDPE, on the other hand, is polymerized from a single ethylene monomer, making its composition relatively simple.
- Structural Differences: ABS has an amorphous structure with irregularly arranged molecular chains, giving it good impact resistance and processability. HDPE has a crystalline structure with orderly arranged molecular chains, giving it high density, high strength, and excellent chemical resistance.
- Performance Differences: The copolymer structure of ABS gives it excellent strength and impact resistance, while the linear structure of HDPE gives it excellent chemical resistance and moisture resistance.
- Application Differences: Due to differences in structure and composition, ABS is often used to manufacture products that require high strength and durability, while HDPE is more suitable for manufacturing packaging materials and pipes with high requirements for chemical resistance and moisture resistance.
What products and industries are ABS and HDPE commonly used in, respectively?
Although ABS and HDPE are both plastics, their unique performance characteristics determine their applications in different products and industries. Understanding their respective application areas helps us better understand the advantages and scope of application of these two materials.
- Electronics and Automotive Industry: ABS, with its excellent impact resistance and ease of processing, is widely used in the manufacture of electronic product housings and automotive interior parts.
- Packaging and Piping Systems: HDPE, with its excellent chemical resistance and moisture resistance, is the preferred material for packaging materials and piping systems.
- Household Appliances and Daily Necessities: ABS and HDPE have their own applications in the field of household appliances and daily necessities. ABS is used for housings and structural components, while HDPE is used for basins, buckets, and simple furniture.
- Agriculture and Industrial Sectors: HDPE is used in the agricultural sector for agricultural films and irrigation pipes, and in the industrial sector for wire and cable sheathing and industrial containers.
What are the differences between ABS and HDPE in terms of processing and molding?

Although ABS and HDPE are both thermoplastics, there are significant differences in the process parameters and methods required during processing and molding due to differences in their physical and chemical properties. Understanding these differences helps us better select the appropriate processing method and improve production efficiency and product quality.
- Temperature Control: ABS has a wide processing temperature range but is sensitive to temperature. HDPE has a narrower processing temperature range but better temperature stability.
- Flowability and Shape: ABS has good melt flowability and is suitable for complex-shaped products. HDPE has relatively poor flowability, which limits the application of complex-shaped products.
- Shrinkage Rate and Precision: ABS has a low shrinkage rate and high product dimensional accuracy. HDPE has a high shrinkage rate and relatively low product dimensional accuracy.
- Processing Methods and Applications: ABS is often used for injection molding and is suitable for complex products. HDPE is often used for extrusion molding and is suitable for pipes and films.
Material characteristics and processing differences
| Feature Comparison | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | Difference Summary |
| Composition & Structure | Copolymer, Amorphous | Homopolymer, Crystalline | Composition and structure differences lead to performance differences |
| Strength Characteristics | High strength, Good impact resistance | High strength, Good chemical resistance | ABS impact resistant, HDPE chemical resistant |
| Processing Performance | Easy to process, Good flowability | Requires higher pressure, Lower flowability | ABS easier to process, HDPE requires higher pressure |
| Typical Applications | Electronics housings, Automotive parts | Packaging, Pipes, Daily necessities | Applications determined by material properties |
Recyclability of ABS and HDPE
Despite the differences in performance and application between ABS and HDPE, their recyclability also has its own characteristics. Understanding the recycling potential of these two materials helps us better assess their impact on the environment.
1.HDPE Recycling Advantages: HDPE has a clear advantage in recyclability due to its wide application and relatively simple recycling process.
2.ABS Recycling Challenges: The ABS recycling process is more complex and requires specialized technology and equipment, so the recycling rate is relatively low.
3.Impact of Technological Progress: With the continuous development of recycling technology, the recycling potential of both ABS and HDPE is gradually increasing.
4.Importance of Collective Efforts: Improving the recycling rate of ABS and HDPE requires the joint efforts of consumers, manufacturers, and recycling facilities.
Conclusion
ABS and HDPE each have their own unique advantages and applications. A thorough understanding of their characteristics and differences will help us make more informed choices in practical applications.
For expert assistance in implementing for your production needs, visit our resource center or contact us. Let’s help you scale up your manufacturing with precision and efficiency!
Post time: Apr-01-2025
